![12 Cannabis Deficiencies [Deficiency Chart, Photos, & Solutions]](https://ogseeds.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/12_Cannabis_Deficiencies_Deficiency_Chart_Photos_Solutions_1200x628-1024x536.jpg)
12 Cannabis Deficiencies [Deficiency Chart, Photos, & Solutions]
Do your cannabis plants grow as well as they should? Are they healthy? Has a nutrient deficiency been detected? Are you unsure? Growing cannabis requires an understanding of nutrient deficiency signs.
When growing cannabis, different nutrient deficiencies have different symptoms, so it is difficult to identify one telltale sign. Some deficiencies manifest as spots, while others manifest as burned tips or varying forms of inflammation.
Here we’ll discuss how to identify and correct nutrient deficiencies, but also check out our resource on what nutrients cannabis plants need. We hope this article will help you understand how to identify and address deficiencies so you can promote healthy root growth and increase nutrient absorption in your plants if they aren’t in peak condition.
Table of Contents
What Is A Cannabis Deficiency?
A cannabis deficiency is a condition where a cannabis plant cannot access or absorb a key nutrient or mineral essential for healthy growth. These essential nutrients are necessary for the plant to grow and produce high-quality buds. A lack of a single essential nutrient can profoundly affect the plant’s bud production and potency.
What Negative Consequences Can Cannabis Deficiencies Have?
Cannabis deficiencies can have several negative consequences, including stunted growth, yellowing leaves, reduced yield, and poor-quality buds. In severe cases, a deficiency can even lead to plant death. It is important to address deficiencies as soon as they are identified to prevent further damage to the plant.
Cannabis Nutrient Deficiency Chart
A nutrient deficiency chart can be a helpful tool in identifying and addressing deficiencies in your cannabis plants. The chart will typically display symptoms of deficiencies and their corresponding deficiencies, making it easy to identify and correct the issue.
For your convenience, we have made this chart to help you with your growing endeavors.
Common Symptoms of Nutrient Deficiency
To correct nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants, the first step is to identify the specific deficiency by looking for the above symptoms and then adjusting the plant’s nutrient intake accordingly. For example, you can correct a nitrogen deficiency by adding more nitrogen-rich fertilizers or supplements to the plant’s diet.
It is also important to note that some cannabis strains may be more prone to deficiencies or excesses of certain nutrients. It is important to research and understand the specific needs of your strain to provide the best care for your plants.
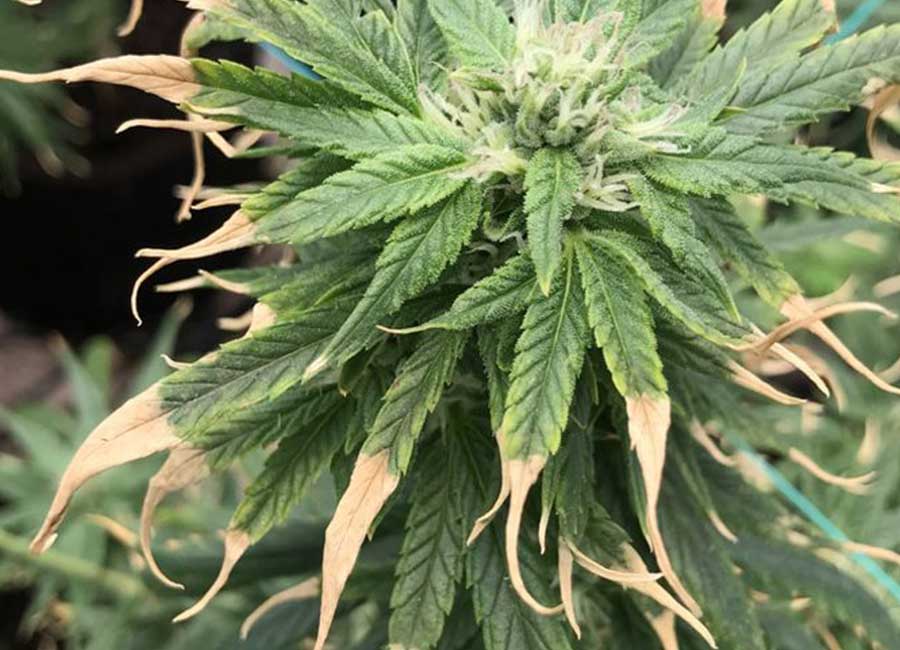

How To Prevent Nutrient Deficiencies in Cannabis Plants
Make sure you follow a proper nutrient schedule and to regularly check the pH levels of the soil or water to ensure that the nutrients are easily accessible to your Cannabis plant. Additionally, it is important to avoid over-fertilizing or under-fertilizing, as this can lead to nutrient lockout or deficiency.
Be aware that you can mistake nutrient deficiencies for other common growing problems such as heat stress, overwatering/underwatering, fluctuating pH levels, ozone damage, and spider mites. It is important to properly diagnose and address these issues to ensure the health and growth of your cannabis plants.
Nutrient deficiencies can significantly impact the health and bud production of your cannabis plants. By identifying and correcting deficiencies, providing the appropriate nutrients and following a proper nutrient schedule, and addressing other common cannabis plant problems, you can ensure that your plants receive the best care possible.
Nutrient Burn
If you ever notice any signs of nutrient burn, you must act immediately to save your crop. First, flush cannabis plants to remove the excess nutrients. Nutrient burn is the exact opposite of a nutrient deficiency since the nutrients are present in the plant’s diet, it is just unable to absorb them properly.
Mobile and Immobile Nutrients In Cannabis Plants
Mobile nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, can be easily transported within the plant. These are essential for growth and can be quickly absorbed by the plant when needed.
Immobile nutrients, such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, cannot be easily transported within the plant. These nutrients are important for structural integrity and overall health, but a deficiency in immobile nutrients will not appear as quickly as it would with your plant’s mobile nutrients.
Understanding the difference between these two types of nutrients is important when diagnosing and treating deficiencies in your cannabis plants.
Spotting Mobile & Immobile Nutrient Deficiencies
A mobile nutrient deficiency will likely show up as discoloration or stunted growth in the newer growth, whereas an immobile nutrient deficiency may be more apparent in older growth.
Your plant can absorb more mobile nutrients than immobile nutrients at one time, so it’s important to have a balanced nutrient schedule to avoid over-fertilizing and nutrient lockout, which can cause other problems in the plant.
Cannabis leaves will show symptoms of mobile nutrient deficiencies near their bases. On the other hand, immobile nutrients will show the first signs of deficiency in newer growth. You can diagnose deficiencies by knowing which nutrients are mobile and immobile.
Cannabis Plant Deficiencies and Excesses Chart
- Nitrogen deficiency: Pale or yellow leaves, slow growth, small or stunted leaves
- Phosphorus deficiency: Dark or purple leaves, slow growth, small or stunted leaves
- Potassium deficiency: Yellow or brown edges on leaves, wilted or curled leaves
- Calcium deficiency: Distorted or curled leaves, brown or black spots on leaves
- Magnesium deficiency: Yellow or brown edges on leaves, wilted or curled leaves
- Zinc deficiency: Slow growth, small or stunted leaves, yellow or pale color on leaves
- Sulfur deficiency: Yellow or pale color on leaves, slow growth, small or stunted leaves
Common Nutrient Deficiencies During The Flowering Stage
Nitrogen is the most common nutrient deficiency in Cannabis plants.
The most common cannabis plant nutrient deficiencies are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Prevent nutrient deficiencies by following a strict nutrient regimen at the appropriate stages of your plant’s life. It’s also important not to feed your plant excess nutrients, as nutrient burn can be just as detrimental as nutrient deficiency. Follow the instructions carefully on any nutrient solution you use. Cannabis plant nutrient deficiencies are very preventable. Mineral deficiencies are a necessary battle to fight as your Cannabis plant cannot produce these minerals on its own.
What Causes Nutrient Deficiency in Cannabis Plants?
Nutrients contain many different elements, and one nutrient plan may lack certain ingredients, or your plants may need more of a certain nutrient than they are getting from your current schedule. Examples of how nutrient deficiencies can look include yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and poor-quality buds.
Cannabis plants require different essential nutrients at different growth phases. Nutrient absorption
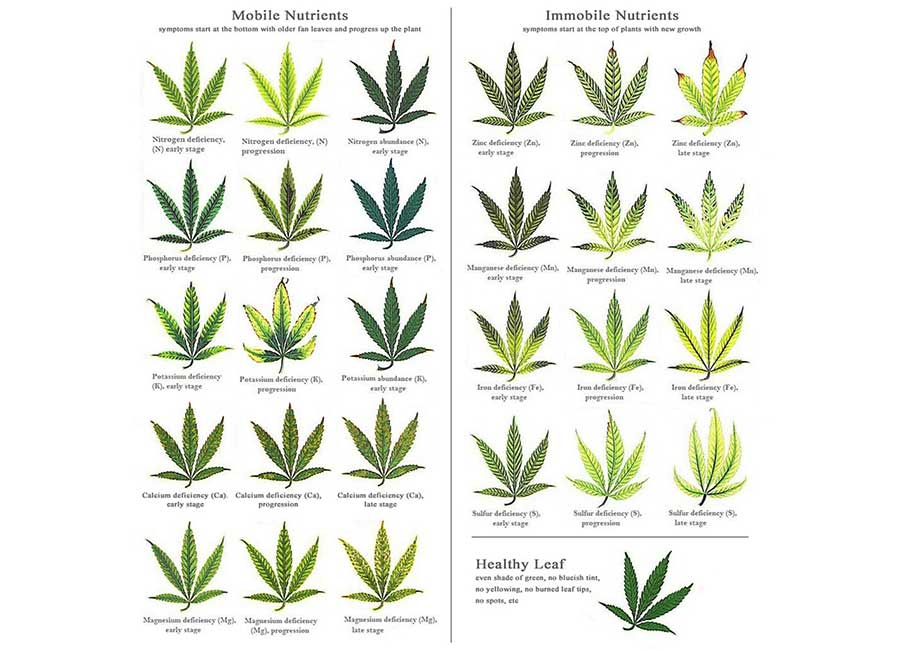
12 Types of Cannabis Nutrient Deficiencies And Solutions
Nutrient deficiencies are a common issue in cannabis cultivation and can be caused by a lack of specific elements in the plant’s diet. We’ve listed the 12 most common nutrient deficiencies in Cannabis plants as well as the solutions to these issues. Being able to identify these issues quickly is a key part of being a great grower. When growing Cannabis, issues are bound to occur no matter how well-dialed your grow room is. Read on to learn how to spot and fix these issues fast
1. Nitrogen Deficiency + Solution
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for cannabis plants and is responsible for the growth of leaves and stems. This nutrient is important throughout your plant’s life, but particularly during vegetative growth. Yellowing leaves and slow growth can identify a nitrogen deficiency. Nitrogen deficiency leads to the yellowing and wilting of your leaves and increased internal temperatures in the plant’s foliage, which causes it to evaporate more moisture through its leaves to cool down.
If your yellowing leaves are at the top or are mostly new growth, you probably don’t have a nitrogen deficiency. It is usually the oldest, lowest leaves that are affected by nitrogen deficiencies or the entire plant that becomes light in color. It is possible for plants to “steal” nitrogen from older, lower leaves to provide it to newer leaves if they don’t get enough nitrogen, which causes the yellowing and wilting of your plant’s leaves when it is nitrogen deficient.
Solution
To correct a nitrogen deficiency, you can add a nitrogen-rich fertilizer to your plant’s diet or use a product specifically formulated to provide a nitrogen boost. Additionally, you can try using organic supplements such as bat guano or worm castings, which are high in nitrogen.
2. Phosphorus Deficiency + Solution
Phosphorus is essential for strong root growth and overall plant health. Dark green leaves with a purple tint and slow growth characterize a phosphorus deficiency.
When your Cannabis plant is deficient in phosphorus, leaves will appear dark blue-green, followed by purpling of the leaf stems. Your plant’s growth will slow considerably both upwards and outwards.
Additionally, you may notice blackish-purple or dark copper spots develop on leaves, and dead spots develop on leaf stems while leaves curl and drop.
Solution
Phosphorus is essential for strong root growth and overall plant health. Dark green leaves with a purple tint and slow growth characterize a phosphorus deficiency. To correct a phosphorus deficiency, you can add a fertilizer high in phosphorus or use a product specifically formulated to provide a phosphorus boost. Organic supplements such as bone meal or rock phosphate can also provide a good source of phosphorus.
3. Potassium Deficiency + Solution
Potassium is essential for the plant’s overall health and is involved in the process of photosynthesis. Yellowing leaves and slow growth characterize a potassium deficiency. If your Cannabis plant is deficient is potassium, you may also notice brown spots on the leaves and a lack of overall vigor.
Solution
To correct a potassium deficiency, you can add a potassium-rich fertilizer to your plant’s diet or use a product specifically formulated to provide a potassium boost. Additionally, you can try using organic supplements such as kelp meal, which is high in potassium.
4. Calcium Deficiency + Solution
Calcium is essential for the plant’s overall health and for the development of strong stems, branches, and your plant’s cell walls. If your Cannabis plant is deficient in calcium, you may notice twisted, distorted leaves and stunted growth. Yellowing leaves and slow growth characterize a calcium deficiency.
Solution
If your plant suffers from calcium deficiencies, add calcium-magnesium supplements to its diet, adjust the pH to 6.2, and add hydrated lime to its watering solution. You can add a calcium-rich fertilizer to your plant’s diet or use a product specifically formulated to provide a calcium boost to correct a calcium deficiency. Additionally, you can try using organic supplements such as eggshells, which are high in calcium.
5. Magnesium Deficiency + Solution
Magnesium is essential for your plant’s overall health and is used for photosynthesis, chlorophyll production, and the development of strong stems and branches. If your plant is deficient in magnesium, it will grow slowly and have yellowing leaves, particularly between the leaf veins.
Solution
To correct a magnesium deficiency, you can add a magnesium-rich fertilizer to your plant’s diet or use a product specifically formulated to provide a magnesium boost. Additionally, you can try using organic supplements such as Epsom salt, which is high in magnesium.
6. Zinc Deficiency + Solution
Zinc is essential for the growth and development of strong stems, branches, and hormone production. A zinc deficiency can be identified by stunted growth and yellowing leaves.
Solution
To correct a zinc deficiency, you can add a zinc-rich fertilizer to your plant’s diet or use a product specifically formulated to provide a zinc boost. Additionally, you can try using organic supplements such as zinc sulfate, which is high in zinc.
7. Iron Deficiency + Solution
Iron is a necessary nutritional element for plants since it’s directly related to energy use by sugars. For chlorophyll production and overall health, cannabis plants need plenty of iron. It’s easy to find iron deficiencies in plants grown in alkaline soils.
The nitrate and sulfate reduction process in cannabis is important for producing chlorophyll and is facilitated by iron (semi-mobile). Iron deficiencies are usually the result of improper pH levels or excess levels of manganese, zinc, or copper. If your cannabis plant is deficient in iron, you will notice the initial symptoms appear in younger growth, with interveinal chlorosis showing at the base of new leaves
Solution
Improve nutrient uptake by flushing your grow medium and giving your plant an iron supplement combined with a bit of nitrogen-rich fertilizer.
8. Manganese Deficiency + Solution
Manganese deficiencies are serious because young leaves develop interveinal chlorosis, dead spots appear, and margins stay dark around interveinal chlorosis. This deficiency in cannabis plants can cause the yellowing of leaves, stunted growth, and a reduction in overall plant health.
Solution
To be sure that the issues you are having with your plant are from Manganese deficiency, test the soil. If the test determines that your plant is Manganese deficient, apply Manganese fertilizers as a foliar spray or soil drench. Make sure to avoid over-application.
9. Sulfur Deficiency + Solution
Sulfur is essential for the production of proteins and is involved in photosynthesis. Yellowing leaves and stunted growth can identify a sulfur deficiency. Although required in very small amounts, this key immobile nutrient contributes to forming vital enzymes and proteins.
Solution
Try dissolving Epsom salts in the water before watering your plants, and adjust your regular water to the proper pH levels. Sulfur deficiency can be fixed by watering your cannabis plant with Epsom salts. The correct mixture of salts to water is 1–2 tablespoons of Epsom salts for every 4–5 liters of water.
10. Molybdenum Deficiency + Solution
Molybdenum deficiency in cannabis turns leaves a pale white, which inhibits photosynthesis. Eventually, they crisp up, and the plant discards them. New growth suffers from a condition known as “whiptail,” leaving them deformed and inefficient.
While it might seem like the damage is purely aesthetic, Molybdenum deficiency is more sinister than merely affecting your Cannabis plants’ looks. If you don’t treat your plants, they’ll stop producing flowers. Any expected bud production can be written off, and whatever you recover will be nearly unusable.
Solution
11. Copper Deficiency + Solution
Copper is an essential micronutrient for cannabis plants, and it can be provided through the use of copper sulfate or other copper-containing fertilizers. It’s important to use the right amount and not overdo it since an excess of copper can be toxic to plants. Copper deficiency symptoms can include pale leaves with brown leaf tips. It can also lead to stunted growth and a lack of resistance to pests and disease.
Solution
Be sure that copper deficiency is the cause of your Cannabis plant issues by testing the soil. If the test determines that your plant is copper deficient, apply Copper sulfate as a foliar spray or soil drench. Make sure to avoid over-application.
12. Boron Deficiency + Solution
A boron deficiency causes the borders of the leaves to dry and brown while the shoots are twisted. In the case of an over-fertilization, the leaves suffer necrosis, causing severe defoliation on the plant.
Solution
To be sure that the issues you are having with your plant are from Boron deficiency, test the soil. If the test determines that your plant is Boron deficiency, apply Boron fertilizers as a foilar spray or soil drench. Make sure to avoid over-application.
Getting the right pH for Cannabis plants
The pH of the soil or water used for cannabis plants should be between 6 and 7 for optimal growth. A pH that is too high or too low can prevent the plant from absorbing the necessary nutrients. It is important to regularly test the pH levels and adjust them as needed.
Can Cannabis Recover From A Deficiency?
Cannabis plants can recover from a deficiency if the problem is identified and corrected promptly. However, the extent of recovery will depend on the severity of the deficiency and the length of time it went untreated.
How Long Can It Take For Cannabis To Recover From A Deficiency?
Correcting deficiencies in cannabis plants can take time, and monitoring your plants closely for any improvement is important. Be sure to follow the instructions on any fertilizers or supplements you use, and keep in mind that it may take several weeks for your plants to recover from not having the necessary nutrients.
How to Fix Nutrient Lockout in Cannabis Plants
Nutrient lockout is a common problem that occurs when the plant cannot absorb the nutrients available in the soil. This can happen when the soil’s pH level is not balanced or the plant is over-fertilized. The symptoms of nutrient lockout include yellowing leaves, slow growth, and a lack of overall health.
The first step in fixing nutrient lockout is to determine the cause of the problem. If the soil’s pH level is too high or too low, it can be corrected by adjusting the pH level to the appropriate range. If the plant is over-fertilized, it is important to reduce the amount of fertilizer used. This will help improve your plants nutrient absorption.
How to Identify Nutrient Lockout in Cannabis Plants
Identify the symptoms of nutrient lockout by looking at the plant’s leaves. Yellowing leaves and slow growth are the most common signs of nutrient lockout. Other symptoms include wilting, discoloration, and a lack of overall health.
How to Prevent Nutrient Lockout in Cannabis Plants
Preventing nutrient lockout is relatively simple. The first step is to ensure that the soil’s pH level is in the appropriate range for the type of plant you are growing. The second step is to avoid over-fertilizing the plant. This can be achieved by using a fertilizer that is designed for Cannabis plants and by following the instructions on the label.
Cannabis Nutrient Deficiencies – Final Thoughts
Being aware of the signs of your sign not receiving the correct nutrients is a key element to being a great Cannabis cultivator. Several common problems that can occur with cannabis plants, including nutrient lockout, heat stress, overwatering/underwatering, fluctuating pH, ozone damage, not enough light, and spider mites.
Knowing how to differentiate these common issues like the ones just mentioned from actual nutrient deficiencies comes with the experience you will gain by cultivating your own Cannabis plants. By identifying the symptoms of these problems and taking the appropriate steps to fix them, you can ensure that your cannabis plants are healthy and produce bud efficiently.










![How Long Does It Take To Grow Cannabis? [Indoors Vs Outdoors]](https://ogseeds.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/How_Long_Does_It_Take_To_Grow_Weed_Indoors_Vs_Outdoors_1200x628-1024x536.jpg)

